Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) - Diagnosis and Treatment
What is Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)?
Anxiety is a common problem when you’re stressed or worried, but when it grows more, lasts for a long time, or becomes uncontrollable, it can affect your daily life. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders, which affects many people globally. Unlike normal anxiety, GAD means feeling more worried all the time about many things such as health, work or any social situations which can last for six months or more. Its goof to understand the causes, recognize the symptoms and explore many effective treatments that can help those with excessive GAD over their lives.
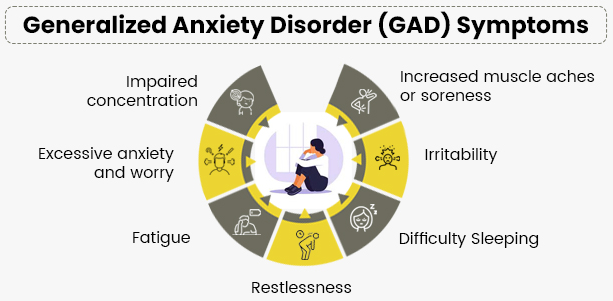
Symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The main symptoms of GAD can be moderate or very intense, but usually including both psychological and physical components:
Psychological Symptoms –
- Excessive worry: We must concern about work, health, family, or everyday events constantly.
- Controlling worry Becomes Difficult: After knowing about the worry or problems, individuals often find it difficult to control it.
- Restlessness: When we are unable to relax or take rest.
- Concentration Difficulty: An individual cant focus or concentrate on their work due to constant worries.
- Irritation: Intense anxiety or worries causes irritation.
- Sleep disturbances: Due to anxiety disorder, individuals become restless, have trouble in falling asleep, or staying asleep.
Physical Symptoms:
- Fatigue: In spite of taking full rest, individuals feel tired due to the disturbance in mind which include constant worries and anxiety disorder.
- Muscle tension: It is detected by persistent muscle tightness, especially in the neck, back, or shoulders.
- Headaches: An individual can get frequent headaches from muscle tension or stress which can lead to constant worry.
- Increased heart rate: Our heart rate gets increased gradually when there is anxiety.
These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making everyday tasks more difficult and stressful.
Causes and Risks of GAD
There are many factors that include the development of anxiety disorder, such as:
- Genetics: Genetics play a main role in GAD development which includes the health history of family. If a close relative, like one of the parent or sibling, has an anxiety disorder, individuals can usually have GAD.
- Biological Factors: Anxiety disorder can be caused due to neurochemical imbalances in the brain, usually with neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). More factors like brain structure, which includes the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, may also influence how anxiety is caused or processed.
- Environmental Issues: Many environmental problems including life events, such as chronic stress, trauma, or sudden changes like a death, or divorce, can lead to intense anxiety disorders. If any individual has gone through tough times in childhood or be in stressful situations for a long time, it can lead to anxiety disorder.
- Personality Traits: The risk of developing higher GAD is for the people who tend that they are perfect, self-obsessed, or have negative outlook on life.
- Health Conditions: Many health conditions may also take part to worse GAD such as thyroid problems, diabetes or heart disease.
Diagnosis of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD can be diagnosed usually through consultation by a healthcare provider, often a psychologist or doctor. The process often includes:
Clinical Interview: There will be a detailed interview conducted by the doctor or therapist, in which he will discuss all the medical history, symptoms, or any family history on anxiety disorder or any other mental health disorders.
Diagnostic Criteria: According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), GAD is diagnosed to a person who experiences intense anxiety and worry for at least six months about various life problems and situations. The anxiety must be difficult to control and related to any of the following symptoms:
• Restlessness
• Fatigue
• Concentration Difficulty
• Irritation
• Muscle tension
• Sleep disturbances
Physical Exam: Physical exam is performed to discard other medical conditions that are causing similar symptoms, including heart disease or thyroid issues.
Psychological Testing: Many high standard tests, like the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) or Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7), can be used to assess the level of anxiety.
Treatment Options for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Effective treatment for GAD usually combines therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Here are the most common options:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) –
CBT is one of the most effective forms of therapy for the treatment of GAD which involves detection and changing negative thoughts that can lead to anxiety. Individuals can reduce their intense worries and develop more solutions for dealing with anxiety problems, which can be done by challenging our thoughts and make them healthier.
Exposure Therapy: It is a part of CBT which involves high level of increase to situations that can lead to anxiety. This may help individuals to learn confronting their fears and reduce to avoid others.
Medication –
Antidepressants: Some medications like Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) are often prescribed to treat GAD by doing balance in serotonin and norepinephrine levels in the brain.
Benzodiazepines: Benzodiazepines (diazepam or lorazepam) may be prescribed for anxiety disorder. These medications can help lessen symptoms quickly but are usually used with caution due to the risk of dependency on them.
Buspirone: If SSRIs or SNRIs do not work well for any individual, then this medication is specifically made for GAD and is a good option for them.
Beta-blockers: They help to manage physical symptoms of anxiety, like a heart disease.
Lifestyle Changes –
Exercise: Regular physical activity or exercises play a main role in reducing anxiety by releasing endorphins, which works as a natural mood booster.
Mindfulness and Relaxation: Individuals can help to reduce stress and get relaxation by practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises.
Sleep Hygiene: Any individual must take healthy sleep, for GAD can be caused often due to sleep disturbances which includes creating a relaxing night routine, maintaining a flexible sleep schedule, and avoid stimulants like caffeine.
Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids can support brain health and improve mood.
Support Groups –
Supporting groups offer a sense of community and provide an opportunity to share experiences with others who understand what it’s like to live with GAD. Family therapy may also be beneficial to help loved ones understand the condition and learn how to provide support.
Conclusion
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) can really affect an individual’s life, but can be controlled with the right treatment and diagnosis. People may learn to be happy and overcome their GAD problems in their productive lives. An individual must ask for help to get better and with the better support ,an individual can overcome it’s problem very easily.
